
Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, USA. McNamara, MS, ICON plc (North Wales, PA, USA) and funded by Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth, NJ, USA. Writing support was provided by Michael S.
#Keynote 042 update trial#
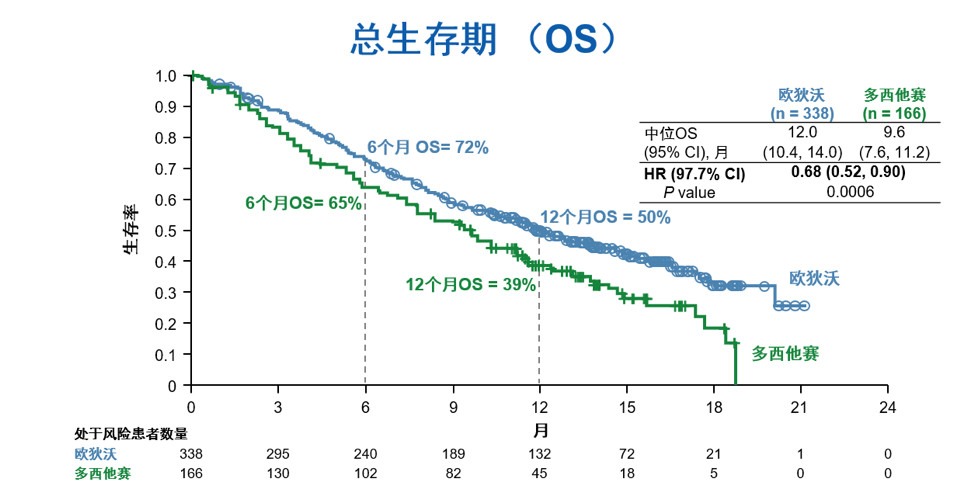
Clinical trial identification Editorial acknowledgement These findings support 1L use of pembro for PD-L1–positive advanced/metastatic NSCLC in China Table: 389P Most pts who completed 2 y of pembro had durable responses. In this longer-term follow-up (∼3 y), 1L pembro monotherapy continued to improve OS with a manageable safety profile vs platinum-based chemo in Chinese pts with locally advanced/metastatic NSCLC without sensitizing EGFR/ALK aberrations and PD-L1 TPS ≥1%. Additional efficacy and safety outcomes will be presented. In 22 pts who completed 35 cycles of pembro, ORR was 77.3% and median DOR was 27.6 mo. Grade 3-5 drug-related AEs occurred in 19.5% of pembro-treated pts vs 68.8% of chemo-treated pts. Pembro improved OS vs chemo in all populations (Table) in pts with PD-L1 TPS ≥1%, the 24-mo rate for OS was 43.8% vs 28.2%, PFS was 15.6% vs 10.6%, and PFS2 was 26.4% vs 8.6%. As of Feb 21, 2020, median time from randomization to database cutoff was 33.0 (range, 25.6‒41.9) mo. ResultsĢ62 Chinese pts with PD-L1–positive NSCLC were enrolled (global, n=92 China extension, n=170) and randomized to pembro (n=128) or chemo (n=134). Primary endpoints were OS in pts with PD-L1 TPS ≥50%, ≥20%, and ≥1%. Pts were randomized 1:1 (stratified by ECOG PS 0/1, squamous/nonsquamous histology, TPS ≥50%/1%‒49%) to up to 35 cycles of pembro 200 mg Q3W or up to 6 cycles of paclitaxel/pemetrexed + carboplatin with optional pemetrexed maintenance (nonsquamous only).

The global and extension studies were designed identically. Here we present an updated analysis of Chinese pts after ∼17 mo additional follow-up. Pembro monotherapy significantly improved OS vs chemo in PD-L1–positive (TPS ≥1%) locally advanced/metastatic NSCLC without targetable EGFR/ALK aberrations in the KEYNOTE-042 global study (NCT02220894) and in an analysis of Chinese pts from the KEYNOTE-042 global and China extension (NCT03850444) studies.

11 Oncology, Merck & Co., Inc., Kenilworth/US.10 Department Of Oncology, Shanghai Pulmonary Hospital, 200433 - Shanghai/CN.9 Respiratory Diseases Department, Zhongshan Hospital Fudan University, Shanghai/CN.8 Department Of Pulmonary Medicine, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin/CN.7 Department Of Respiratory Medicine, Xiangya Hospital Central South University, Hunan/CN.6 Stem Cell And Cancer Center, The First Hospital of Jilin University, Changchun, Jilin/CN.5 Department Of Medical Oncology, Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center, 510060 - Guangzhou/CN.4 Respiratory Department, The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang University, Hangzhou/CN.3 Department Of Medical Oncology, Zhejiang Cancer Hospital, Hangzhou/CN.2 Department Of Respiratory Medicine, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Bejing/CN.1 Department Of Pulmonary Oncology, Guangdong Lung Cancer Institute, 510000 - Guangzhou/CN.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
